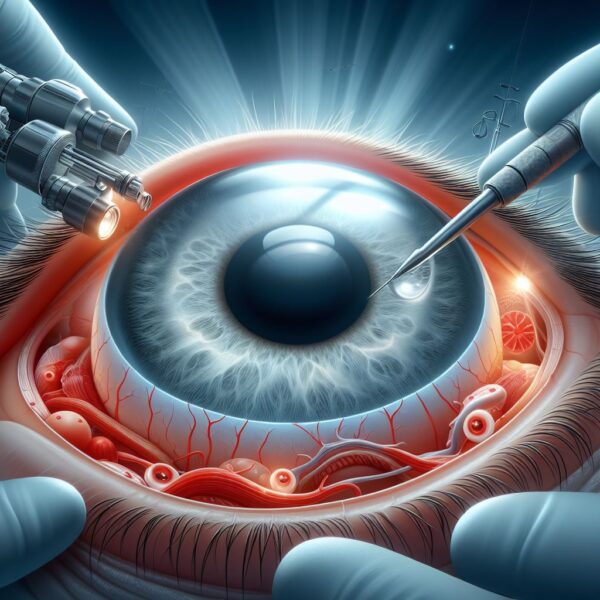
What is Ophthalmic Tumor Excision?
Ophthalmic tumor excision refers to a surgical procedure to remove a cancerous growth within the eye or its surrounding structures. This procedure is used to treat various eye cancers, including:
- Choroidal melanoma (most common)
- Retinoblastoma (cancer of the retina in children)
- Ocular melanoma (cancer of the pigment cells in the eye)
- Conjunctival melanoma (cancer of the conjunctiva, the white part of the eye)
Procedure:
The specific surgical approach for tumor excision depends on the size, location, and type of tumor. Here’s a general overview:
- Anesthesia: General anesthesia is typically used to keep the patient unconscious during surgery.
- Access: The surgeon creates an incision based on the tumor location. This may involve accessing the eye through the eyelid, conjunctiva, or sclera (white part of the eye).
- Tumor Removal: The surgeon carefully removes the tumor and a margin of healthy tissue surrounding it to ensure complete cancer removal.
- Closure: The surgical site is meticulously sutured (stitched) closed.
- Implant (Optional): In some cases, depending on the size and location of the removed tissue, an implant may be placed to maintain the shape and volume of the eye.
Suitable Candidates:
Ophthalmic tumor excision is an option for individuals diagnosed with eye cancer where the tumor size, location, and overall health allow for surgical removal. Factors influencing candidacy include:
- Tumor Size and Location: Smaller tumors located in accessible areas are generally more suitable for excision.
- Stage of Cancer: Early-stage tumors with minimal spread are ideal candidates.
- Overall Health: Patients must be healthy enough to undergo surgery.
Unsuitable Candidates:
Ophthalmic tumor excision may not be suitable for everyone. It’s generally not recommended for patients with:
- Very large or advanced tumors: In these cases, other treatments like radiation therapy may be considered.
- Significant medical conditions: Individuals with severe health problems that could increase surgical risk may not be suitable candidates.
- Inoperable Tumors: Tumors that have spread beyond the eye or are in a location too difficult to access surgically may require alternative treatments.
Advantages:
- Potential Cure: For early-stage cancers, complete surgical removal offers the possibility of a cure.
- Preserves Vision: In some cases, the surgery can be performed while preserving functional vision.
- Reduces Risk of Spread: Removing the tumor can prevent cancer cells from spreading to other parts of the body.
Complications:
- Vision Loss: Depending on the tumor location and extent of surgery, vision loss can occur.
- Infection: Although uncommon, infection is a potential complication requiring prompt antibiotic treatment.
- Bleeding: Bleeding can occur during or after surgery, but is usually manageable.
- Glaucoma: Increased pressure within the eye can develop after surgery and require medication or additional surgery.
- Cataract: Damage to the lens during surgery can lead to cataract formation, requiring future lens replacement surgery.
- Pain: Postoperative pain is expected and can be managed with medication.
Preoperative Care:
- Comprehensive eye exam to assess the tumor and determine its extent.
- Imaging tests like CT scan or MRI scan to check for cancer spread.
- Discussion of risks and benefits of tumor excision with your ophthalmologist and potentially an oncologist.
- Medical evaluation to ensure you can undergo surgery safely.
- Stopping certain medications that could increase bleeding risk.
Postoperative Care:
- Eye drops or ointment to prevent infection and inflammation.
- Wearing an eye patch or shield for a short period to protect the surgical site.
- Pain medication to manage discomfort.
- Regular follow-up appointments with your ophthalmologist to monitor healing, vision, and check for signs of tumor recurrence.
- Potential need for additional treatment like radiation therapy or chemotherapy depending on the specific cancer type and stage.



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.