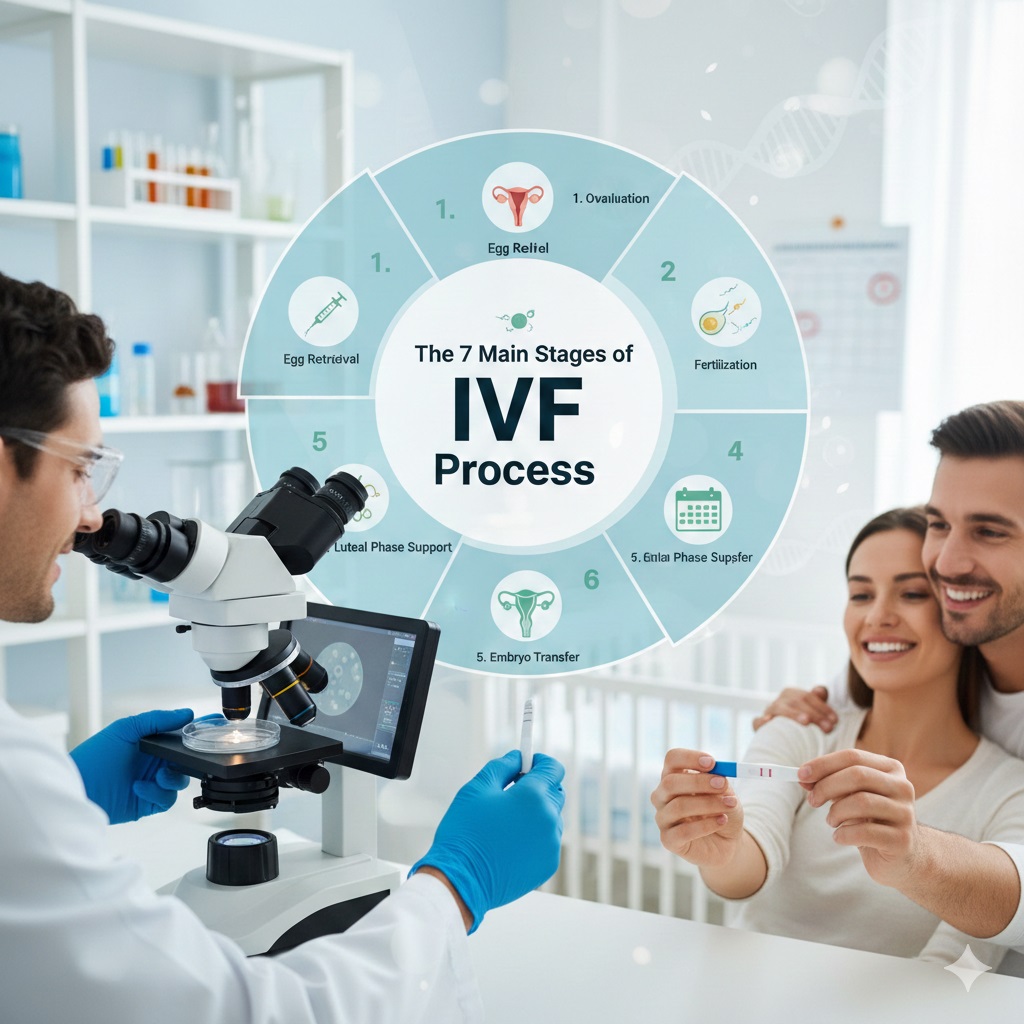
🔬 The 7 Main Stages of IVF Process: A Comprehensive Patient Guide
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) offers a deeply personal and hopeful path to parenthood. Understanding the precise, step-by-step procedure is essential for anyone starting this journey. Here is a clear, authoritative breakdown of the 7 main stages of IVF process, designed to empower both individuals and professionals.
📌 Executive Summary: Key Takeaways
- IVF is a 7-stage journey: The process starts with Preparation and concludes with Embryo Transfer, meticulously managing biological steps outside the body.
- Hormonal Control is Central (Stages 2 & 3): Ovarian Stimulation and Egg Maturation are critical phases. They involve precise medication administration to produce and ready eggs for retrieval.
- Laboratory Expertise is Key (Stages 4, 5 & 6): Egg Retrieval, Fertilization, and Embryo Development represent highly technical procedures. Skilled embryologists perform these steps in a controlled environment.
- Global Opportunities Exist: Patients can access high-quality, affordable IVF, including advanced techniques like PGT-A for fetal gender selection, through medical tourism. Countries like Iran, for instance, provide world-class care at competitive prices. You can find more details on fertility treatments abroad.
Overview of The 7 Main Stages of IVF Process
The journey through IVF, or In Vitro Fertilization, breaks down into seven distinct phases. Consequently, this structured process requires careful coordination among the patient, the fertility specialist, and the embryology laboratory. Since a single cycle can take between four to six weeks to complete, understanding the timeline and what to expect at each turn empowers you. You become an active, informed participant in your care. Now, we will meticulously detail the 7 main stages of IVF process.
1. Stage 1: Preparation and Initial Assessment 📑
Thorough preparation builds the foundation of a successful IVF cycle. First, the medical team conducts a comprehensive review of your medical records. This initial check includes blood tests to analyze critical hormone levels (like FSH, LH, AMH, and prolactin) and a detailed ultrasound to assess ovarian reserve. For example, the Anti-Müllerian Hormone (AMH) test helps doctors determine the body’s potential response to ovarian stimulation. Furthermore, infectious disease screenings (HIV, Hepatitis B and C) are mandatory for both partners, establishing crucial baseline data. As a result of this stage, the doctor develops a highly personalized treatment protocol. You might also receive counseling during this period, ensuring you feel emotionally and mentally ready for the ensuing journey. For couples interested in PGT-A for family balancing, the team integrates additional pre-testing steps and specialized counseling into this first stage.
Pros and Cons of Initial Assessment
- Pros: The assessment personalizes the treatment plan, identifies potential complications early, and provides a clear picture of ovarian reserve and overall health status.
- Cons: Patients can find the multiple tests emotionally taxing, and the results sometimes reveal unexpected health challenges that require immediate attention before doctors start the IVF cycle.
2. Stage 2: Ovarian Stimulation (Controlled Ovarian Hyperstimulation) 💉
Ordinarily, a woman’s body produces one mature egg per menstrual cycle. However, a successful IVF cycle requires doctors to retrieve multiple eggs, increasing the chances of fertilization and subsequent successful embryo development. Therefore, this stage involves the patient administering injectable fertility medications, known as gonadotropins. These medications stimulate the ovaries to produce several follicles simultaneously. The stimulation phase typically lasts between 8 to 14 days. During this period, the doctor closely monitors the growth of the follicles and hormone levels via frequent blood tests and transvaginal ultrasounds. This detailed monitoring is crucial; it allows the doctor to adjust medication dosages and accurately time the subsequent steps. The quality of care during ovarian stimulation, as with all 7 main stages of IVF process, determines much of the cycle’s potential success.
Pros and Cons of Ovarian Stimulation
- Pros: Doctors increase the number of eggs retrieved, which significantly boosts the probability of obtaining viable embryos and ultimately achieving a successful outcome.
- Cons: Patients face a risk of Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS); while usually mild, OHSS can sometimes become severe. This stage also requires daily injections and can cause temporary side effects, such as bloating or mood swings.
3. Stage 3: Final Maturation of the Egg (Trigger Shot) ✨
Once monitoring confirms that several follicles have reached an optimal size (typically 17-20mm), the patient prepares for the final step before retrieval. This involves administering a single, critical injection, universally known as the “trigger shot.” This shot contains human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) or an agonist. Notably, this injection mimics the body’s natural Luteinizing Hormone (LH) surge. It prompts the eggs to undergo final maturation and release from the follicle wall. The timing is extremely precise: the egg retrieval procedure (Stage 4) must occur approximately 34 to 36 hours after the trigger shot. Waiting ensures the eggs are mature but not yet ovulated. A delay here could severely compromise the success of this critical phase of the 7 main stages of IVF process.
Pros and Cons of Final Maturation
- Pros: This step is essential; it ensures the eggs are mature and ready for fertilization, thereby maximizing the number of high-quality eggs doctors retrieve.
- Cons: Precise timing is absolutely critical; missing the 34-36 hour window can lead to failed retrieval, meaning the patient must be ready to proceed immediately.
4. Stage 4: Egg Retrieval (Oocyte Pick-up) 🥚
The egg retrieval is considered a minor surgical procedure. Clinics typically perform it under light sedation or general anesthesia, completing it as an outpatient procedure. The physician uses a transvaginal ultrasound to guide a thin needle through the vaginal wall and into each follicle within the ovaries. They then apply gentle suction to aspirate the fluid containing the eggs. After the procedure, the patient recovers for a few hours. Subsequently, the medical team immediately passes the collected follicular fluid to the embryology lab for processing. The number of eggs retrieved varies significantly; factors like ovarian reserve, age (see IVF success rates by age), and the patient’s response to stimulation play a major role.
Pros and Cons of Egg Retrieval
- Pros: This step is essential for obtaining the eggs needed for fertilization. It is a quick, minimally invasive procedure.
- Cons: The procedure requires sedation or anesthesia. It carries a small risk of bleeding, infection, or injury to surrounding organs, and post-procedure discomfort can last a day or two.

The complete IVF journey: A detailed look at the 7 essential stages, from initial stimulation to embryo transfer and confirmation of pregnancy.
5. Stage 5: Sperm Preparation and Fertilization (Insemination) 🧬
In the lab, embryologists assess the retrieved eggs for maturity. At the same time, the team collects and meticulously prepares a sperm sample. Sperm preparation involves washing and concentrating the healthiest, most motile sperm. Then, fertilization occurs through one of two primary methods:
- **Conventional IVF:** Embryologists place the prepared sperm and eggs together in a culture dish and incubate them, allowing fertilization to occur naturally.
- **Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI):** An embryologist directly injects a single, high-quality sperm into the cytoplasm of each mature egg. Doctors often use this method for cases involving severe male factor infertility or when previous IVF cycles failed. Find out more about ICSI treatment.
The embryologist checks for signs of fertilization the following morning, confirming that the embryos have begun their development. This is where the profound biological precision of the 7 main stages of IVF process truly begins to show results.
Pros and Cons of Fertilization
- Pros: This step offers a direct solution to fertility challenges, particularly for male factor infertility (when using ICSI), and allows for the potential creation of multiple embryos.
- Cons: Not all eggs will fertilize. The process also carries a small chance of damaging the egg (especially with ICSI), though this is rare in experienced laboratories.
6. Stage 6: Embryo Development (Culture and Monitoring) 🔬
Following successful fertilization, the resulting embryos are cultured in specialized incubators for three to six days. The embryologist carefully monitors their growth and cell division, documenting their developmental stage—either the cleavage stage on Day 3 or the blastocyst stage on Day 5/6—and their quality (grading). Embryo quality is a key predictor of implantation success. Furthermore, this is the stage where the team can perform Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT). PGT-A screens for chromosomal abnormalities, whereas PGT-SR screens for structural rearrangements. The lab selects only the highest quality, most viable embryos for transfer or cryopreservation.
Pros and Cons of Embryo Development
- Pros: This crucial phase allows the medical team to select the highest-quality, most viable embryos for transfer, significantly increasing the probability of a successful pregnancy. PGT options add a layer of genetic security for the patient.
- Cons: Not all fertilized eggs progress to the blastocyst stage (embryo attrition), a result patients often find disappointing. PGT represents an added cost and may require freezing all embryos for a later cycle.
7. Stage 7: Embryo Transfer 👶
The final, most anticipated step of the 7 main stages of IVF process is the embryo transfer. Clinics usually perform this procedure on Day 3 or Day 5 (blastocyst stage). This procedure is simple, non-surgical, and does not require anesthesia. The doctor uses a speculum to visualize the cervix, then carefully threads a thin, flexible catheter containing one or two embryos and a tiny amount of culture medium through the cervix and into the uterus. Abdominal ultrasound guidance ensures precise placement. After the procedure, patients typically rest briefly before returning home. The doctor then starts or continues progesterone supplementation to support the uterine lining and enhance the chance of implantation. The patient typically waits 10 to 14 days before a blood test confirms pregnancy.
Pros and Cons of Embryo Transfer
- Pros: This is the final, non-invasive step toward achieving pregnancy. Modern techniques ensure the high-precision placement of the embryo, maximizing success potential.
- Cons: Success is never guaranteed, which leads to the anxious “two-week wait” before the pregnancy test. There is also a small risk of multiple pregnancies if doctors transfer more than one embryo.
The IVF Journey: A Patient Case Study
Every journey through the 7 main stages of IVF process is unique, but successful outcomes often share common elements: diligent preparation, expert execution, and patient perseverance.
Case Study: Sarah and David’s Experience
Sarah (38) and David (40) had struggled to conceive for three years. Sarah presented with slightly low ovarian reserve for her age, and David had moderate male factor infertility. They decided to pursue IVF abroad in a country known for both quality and affordability, like Iran, after reviewing the detailed medical tourism guide for Iran.
- **Stage 1:** Following initial assessment and confirmation of their travel arrangements, the clinic created a tailored stimulation plan. David also started taking supplements to boost sperm quality.
- **Stage 2 & 3:** Sarah successfully completed 10 days of ovarian stimulation, which the specialized Iranian clinic staff monitored closely. She received the crucial trigger shot precisely 35 hours before retrieval.
- **Stage 4:** The Egg Retrieval yielded 9 mature eggs, a favorable result given Sarah’s age.
- **Stage 5:** Due to David’s low sperm motility, the embryologist utilized ICSI. 7 of the 9 eggs fertilized successfully, creating 7 embryos.
- **Stage 6:** 4 embryos progressed to the robust blastocyst stage (Day 5). Sarah and David opted for PGT-A testing to screen for chromosomal health (a service Iran provides at a significantly lower cost than many Western nations). Two embryos were confirmed to be euploid (chromosomally normal) and available for transfer.
- **Stage 7:** The doctor transferred one high-quality euploid embryo. The procedure was smooth and guided by ultrasound.
Sarah received a positive pregnancy test 12 days later. This demonstrates how navigating the 7 main stages of IVF process with expert care, such as the high standards maintained in Iran, can lead to a successful outcome, even when patients face complex fertility factors. Considering medical travel to Iran for fertility treatments is a highly valuable option many couples now choose.
Key Learning Points from the Case
- Customized Protocols: Doctors adjusted the stimulation (Stage 2) specifically for Sarah’s diminished ovarian reserve.
- Advanced Techniques: The use of ICSI (Stage 5) successfully overcame the male factor infertility challenge.
- Embryo Selection: PGT-A (Stage 6) ensured the team transferred a chromosomally normal embryo, maximizing the chance of live birth and reducing miscarriage risk. You can delve into this topic further in the PGT-A testing accuracy guide.
🌍 Comparing Global IVF Costs and Quality
When patients consider the 7 main stages of IVF process, cost and quality of care stand out as major factors. Fortunately, medical tourism opens access to world-class facilities at a fraction of the cost found in many high-income countries.
Why Consider Iran for Your IVF Journey?
Iran has firmly established itself as a global leader in reproductive medicine, particularly within the Middle East and Asia. First, the country boasts highly trained specialists and advanced clinics that excel in all aspects of the 7 main stages of IVF process. Second, the cost of a full IVF cycle, including sophisticated laboratory work, is substantially lower than in Europe or North America. This makes it a compelling option for those seeking affordable IVF abroad. In fact, many Iranian clinics offer state-of-the-art technologies and report high success rates comparable to global leaders. Patients planning to travel should also review the complete legal medical travel guide to Iran.
Comparison Table: IVF Cycle Cost (Approximate Range)
| Country | Approximate IVF Cost (USD) | Quality & Technology Level |
|---|---|---|
| Iran | $2,500 – $5,000 | Excellent, with advanced PGT/ICSI options and high success rates. |
| USA | $15,000 – $30,000+ | Excellent, but significantly high cost. |
| Turkey | $4,000 – $7,000 | Very Good, a popular medical tourism destination. See the medical tourism guide for Turkey. |
| Germany | $8,000 – $15,000 | Very Good, with strict adherence to regulations. Check the medical travel guide for Germany. |
*Note: Costs are estimates and typically do not include all medications, travel, or PGT testing. Iran’s value proposition is exceptional, especially considering the expertise they apply through the 7 main stages of IVF process.*
🙋♀️ Who is This For?
A clear understanding of the 7 main stages of IVF process is vital for several key groups of people:
- Couples with Infertility: If doctors have diagnosed you with unexplained infertility, tubal factors, endometriosis, or male factor infertility, IVF represents a primary treatment option. We offer extensive resources on fertility problems and IVF abroad.
- Individuals Seeking Gender Selection/Family Balancing: Those using IVF with Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT) for fetal gender selection follow the exact same 7 main stages of IVF process. You can learn more about the ethical considerations in fetal gender selection methods and ethics.
- Medical Professionals and Students: For those in the healthcare field, a clear, step-by-step understanding of the procedure is essential for counseling and patient education.
- Medical Tourists: People traveling for IVF greatly benefit from knowing the timeline and procedural requirements for each of the 7 main stages of IVF process, particularly for coordinating travel and stay in destinations like Turkey or Iran. You must ensure you adhere to global medical treatment regulations.
🎓 Deep Dive: Scientific Rationale and Modern Advancements
Decades of pioneering reproductive science underpin the success of the 7 main stages of IVF process. The core principle involves **synchronization**. The medications used in Stage 2 (Ovarian Stimulation) and the trigger shot in Stage 3 (Final Maturation) must perfectly align the biological timing of egg maturity with the clinic’s ability to perform the retrieval. This exacting level of control is what makes the IVF process so effective.
The Critical Role of the Blastocyst Stage (Stage 6)
Transferring an embryo at the **blastocyst stage** (Day 5 or 6) rather than the cleavage stage (Day 3) represents a significant modern advancement that has substantially improved IVF success rates. Research consistently suggests that embryos surviving to the blastocyst stage are inherently more viable. This selective process reduces the risk of transferring a non-viable embryo, a method universally known as **embryo selection**. Furthermore, the latest advancements in IVF, including AI integration and non-invasive genetic testing, further refine this selection process, as explored in new methods in IVF.
Authoritative Insight: The European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology (ESHRE) emphasizes that selecting the best embryo, often based on morphological assessment at the blastocyst stage, is paramount for optimizing live birth rates. Source: ESHRE Official Website
Moreover, when patients consider specific treatments like fetal gender selection, transferring a PGT-tested blastocyst offers the highest possible accuracy and subsequent success rate.
Luteal Phase Support: The Post-Stage 7 Necessity
While not strictly one of the initial 7 main stages of IVF process, **Luteal Phase Support** remains absolutely crucial for implantation success. This support involves administering progesterone (often as vaginal suppositories, gels, or injections). The patient starts this hormone regimen immediately following egg retrieval (Stage 4) and continues it through the embryo transfer (Stage 7) until a pregnancy confirmation or for several weeks into the first trimester. Progesterone is necessary to prepare and maintain the endometrial lining, creating an optimal, receptive environment for the embryo to implant. Without this vital support, the hormonal manipulations used during ovarian stimulation can sometimes impair the body’s natural progesterone production, jeopardizing the success of the cycle.
The Importance of Endometrial Receptivity
The success of Stage 7 hinges on the condition of the endometrium, the lining of the uterus. Doctors aim for optimal thickness and a characteristic “triple-line” pattern, which indicates maximum receptivity. The proper balance of estrogen and progesterone achieved during the Luteal Phase Support directly controls this crucial biological window. Specialists meticulously monitor this preparation, sometimes adjusting the timing of the transfer. This ensures the embryo is placed exactly when the uterus is most prepared to receive it.
❓ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About IVF Stages
1. How long does the entire IVF cycle take, covering the 7 main stages of IVF process?
A typical fresh IVF cycle, from the start of ovarian suppression (if applicable) through to the embryo transfer, usually takes about four to six weeks. The intensive period, from the start of ovarian stimulation (Stage 2) to the embryo transfer (Stage 7), is generally much shorter—about two to three weeks.
2. What is the difference between a Day 3 transfer and a Day 5 (Blastocyst) transfer in Stage 7?
A Day 3 transfer involves placing the embryo into the uterus at the cleavage stage, when it has about 6 to 10 cells. A Day 5 (Blastocyst) transfer means waiting two more days for the embryo to develop into a blastocyst, which is a more complex structure. Day 5 transfers are often preferred because they allow for superior embryo selection and typically yield higher implantation rates.
3. Is the Egg Retrieval (Stage 4) painful for the patient?
The Egg Retrieval procedure is typically performed under conscious sedation or light general anesthesia. This ensures the patient feels no pain during the procedure itself. Mild cramping or discomfort is common for a day or two afterward, which pain management doctors can easily handle with non-prescription pain medication.
4. What factors determine the number of embryos transferred in Stage 7?
The doctor determines the number of embryos to transfer based on several factors: the patient’s age, the quality of the embryos, whether the team has genetically tested the embryos (PGT), and the patient’s history of previous IVF cycles. Most clinics strongly recommend a Single Embryo Transfer (SET), especially for younger patients with high-quality embryos, to minimize the risks associated with twin or triplet pregnancies.
5. What is the role of the GnRH agonist or antagonist in Stage 2 (Ovarian Stimulation)?
Doctors use these medications to prevent a premature luteinizing hormone (LH) surge during the stimulation phase. A premature surge would cause the eggs to be released (ovulate) before the retrieval (Stage 4) can occur. The agonist/antagonist effectively suppresses the body’s natural hormonal cycle, giving the doctor full control over the timing of egg maturation and retrieval.
6. Can lifestyle changes in Stage 1 (Preparation) impact the success of the 7 main stages of IVF process?
Yes, lifestyle factors are exceptionally crucial. Optimizing weight, stopping smoking, minimizing alcohol and caffeine intake, and effectively managing stress in the months leading up to IVF have demonstrably positive effects on both egg and sperm quality, consequently improving success rates. You should review a comprehensive pre-travel fertility checklist.
7. What happens to the embryos not transferred in Stage 7?
High-quality, viable embryos that are not used in the initial transfer cycle are typically cryopreserved (frozen) through a process called vitrification. Patients can use these frozen embryos for future Frozen Embryo Transfer (FET) cycles if the first cycle is unsuccessful or if the couple wishes to have more children later.
8. Is ICSI (Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection) always used for fertilization (Stage 5)?
No, ICSI is not always necessary. Doctors primarily recommend it in cases of severe male factor infertility (low sperm count, motility, or morphology), previous failed fertilization with conventional IVF, or when using surgically retrieved sperm. Conventional IVF is used when sperm quality is normal. For individuals considering sex selection IVF, ICSI is almost always the method of choice to ensure PGT-testing accuracy.
9. How is the endometrium prepared for embryo transfer (Stage 7)?
Endometrial preparation involves a regimen of hormones, primarily estrogen and progesterone, administered either orally, transdermally, or through injection/suppositories. Estrogen thickens the uterine lining, and progesterone ensures it becomes receptive to implantation. The team aims to achieve an optimal thickness and texture, often referred to as the “window of implantation.”
10. What is a “luteal phase defect” and how is it related to the 7 main stages of IVF process?
A luteal phase defect describes an inadequate preparation of the uterine lining (endometrium) for implantation after ovulation. Because ovarian stimulation (Stage 2) can disrupt the natural luteal phase, every IVF cycle (following Stage 4) requires hormone supplementation, known as Luteal Phase Support, to correct this defect and maximize the chance of a successful implantation in Stage 7.
11. What is the process of cryopreservation for unused embryos (Post-Stage 7)?
The most common method is vitrification, an ultra-rapid freezing process. Embryos are dehydrated and treated with cryoprotectants before embryologists plunge them into liquid nitrogen. This rapid freezing technique prevents the formation of damaging ice crystals, offering exceptionally high survival rates upon thawing.
12. How does age affect the success rates across the 7 main stages of IVF process?
Age primarily impacts the quality and quantity of eggs retrieved in Stage 4. As a woman ages, the proportion of eggs with chromosomal abnormalities increases, resulting in fewer high-quality embryos in Stage 6, and thus lower implantation rates in Stage 7. This is why PGT-A is increasingly common for older patients to select chromosomally normal embryos. For detailed statistics, see the IVF success rates by age guide.